Today’s marketing landscape is mired with uncertainty for consumers and companies alike. As the digital ecosystem expands and data becomes more fragmented, businesses face the challenge of understanding and optimizing their marketing efforts for growth and profitability. According to eMarketer, one-fifth of companies believe that 50% of the information received by third-party data brokers is inaccurate.
Marketing mix modeling (or MMM) can serve as a compass for marketers, guiding them in optimizing their strategies for maximum ROI. Drawing on a wealth of varied data and honing in on an objective that’s key to your business, MMM can create cohesive strategies that maximize reach, engagement, and conversions.
Jump To:
What is marketing mix modeling?
Marketing mix modeling is an analytical model that marketers use to better understand the impact of different marketing activities on sales and other market share. The concept originated in the 1960s, was adopted by large companies in the 1990s, and has continued to evolve as digital analytics and tracking have advanced.
At its core, MMM answers fundamental questions about the effectiveness of various marketing elements, including advertising, promotions, pricing strategies, and distribution channels. By analyzing historical data and the impact of each element, marketers can make informed decisions about their multichannel marketing strategy, optimizing their marketing mix and maximizing their reach, engagement, conversions, and ROI.
Marketing mix modeling vs media mix modeling
Marketing mix modeling shouldn’t be confused with media mix modeling, despite the MMM acronym. While they’re both analytical approaches to marketing that help you better understand the impact of your marketing efforts, they have different focuses and methodologies.
Marketing mix modeling analyzes various marketing elements beyond media channels to optimize overall marketing strategy. In contrast, media mix modeling focuses on optimizing the allocation of advertising budgets across different media channels to improve advertising effectiveness.
The marketing mix modeling process
If you’re just starting with marketing mix modeling, it’s important to define your objectives and primary KPIs. Your objective can range from increasing market share, brand awareness, or sales.
Next, an agency partner or data scientist will gather the relevant information needed for your objective. This can come from different sources, such as sales, marketing spend, impressions, pricing, and external factors like competitor activity or economic data.
Once the data has been gathered, they’ll select the appropriate marketing mix model and factors that will work best for your objective.
Components of marketing mix modeling
There are multiple factors that influence marketing mix modeling. These can include:
Multi-linear regression modeling
Multi-linear regression is a statistical modeling technique that analyzes multiple independent variables (like advertising spend, price, or the economy) to explain the variation in a dependent variable (like sales, revenue, or market share). Multi-linear regression models in MMM are used to understand the relationships between marketing inputs and sales outcomes while factoring in other elements that may affect sales, such as seasonality, economic conditions, and industry trends.
By analyzing the impact associated with each of these factors, marketers can determine the strength and direction of their impact on sales and identify opportunities for optimization.
Multivariate analysis
Multivariate analysis refers to a statistical technique that involves the analysis of multiple variables to gain a better understanding of their relationships and interactions. For MMM, multivariate analysis helps marketers analyze the combined impact of different marketing activities on sales or other KPIs while also accounting for how each of these efforts impacts the other.
Multivariate analysis enables marketers to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations in their data that may not be apparent through other analyses, providing deeper insights into the market dynamics and consumer behavior.
Multiple regression analysis
Multiple regression analysis helps clarify the relationship between marketing efforts (like ad spend, promotions, pricing, and sales) and a single outcome (like revenue).
By leveraging multiple regression models in MMM, marketers can gain deeper insights into what’s driving sales performance and develop more effective marketing strategies to achieve their business goals.
Linear and nonlinear impact of predictors
A model with linear impact shows that the relationship between a predictor variable (an increase in advertising spend) and the outcome variable (a rise in sales) is proportional and follows a straight line. Linear relationships are straightforward to interpret and model because the cause and effect are clear.
Predictor impact can also be nonlinear, which means that the relationship between the predictor (an increase in advertising spend) and outcome (sales remaining stagnant) aren’t proportional and don’t have a clear pattern.
By incorporating nonlinear effects into the modeling process, marketers can better understand the complexity of consumer behavior and make more accurate predictions and recommendations for optimizing the marketing mix.
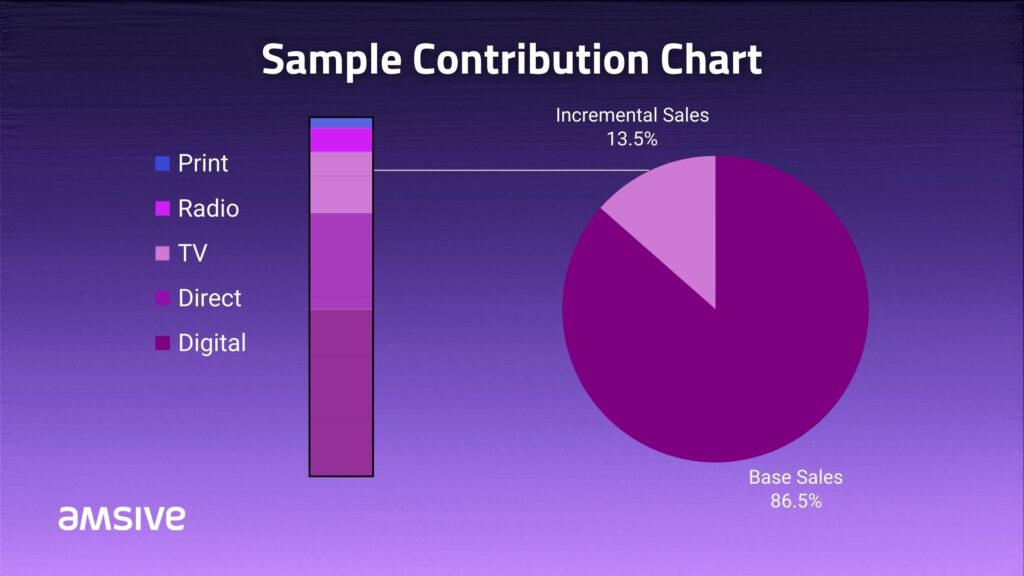
Base sales and incremental sales
Baseline sales and incremental sales help marketers understand the drivers of overall sales performance.
Baseline sales are the underlying demand for a product or service driven by factors such as brand awareness, consumer preferences, and market conditions. Baseline sales are typically estimated using historical sales data during periods of minimal marketing activity, such as off-seasons or periods without promotional campaigns.
Incremental sales, on the other hand, are the additional sales generated because of specific marketing activities or interventions. This captures the impact of marketing inputs like advertising, promotions, pricing strategies, or new product launches on total sales performance. Incremental sales are calculated by comparing actual sales during periods of marketing activity to the expected base sales level.
Understanding these two sale types allows marketers to understand the contributions of different marketing activities to overall sales performance.
Advertising and media modeling
In MMM, marketers analyze the impact of advertising and media spending on their KPIs to understand the effectiveness of their campaigns and optimize their marketing strategies. They also analyze multichannel marketing effects and the effectiveness of their media mix optimization.
By understanding the relationship between advertising expenditures and sales outcomes, marketers can assess the ROI of their advertising efforts and make data-driven decisions about resource allocation and campaign optimization.
Promotions and pricing
Understanding the impact of promotions and pricing on sales performance helps marketers understand how effective their promotional activities (like discounts and coupons) and pricing decisions (like competition and demand) and optimize their strategies accordingly.
Promotions and pricing analysis in MMM provides marketers with valuable insights into the effectiveness of their promotional activities and pricing decisions, opportunities for optimization, and strategies to achieve their sales and profitability goals.
New product launches
Analyzing the effectiveness of a new product launch can help marketers understand the effectiveness of their launch strategies and optimize their marketing efforts. A new product launch can involve additional marketing efforts, including ad campaigns, PR, social media promotion, influencer marketing, product demonstrations, and sampling programs.
By measuring metrics like brand lift, purchase intent, and trial rates, marketers can identify high-performing tactics and refine their launch strategies to maximize impact.
Competition
Competition influences the effectiveness of marketing strategies and the allocation of resources across channels. Analyzing competitors’ activities, market share, and positioning helps marketers understand the landscape and identify opportunities or threats. By understanding the competitive landscape, marketers can assess the relative performance of their own marketing initiatives and make informed decisions to stay ahead of competitors.
Contribution charts
Contribution charts offer a visual representation of the impact of different marketing activities on overall business performance. These charts allow marketers to assess how each marketing channel or campaign contributed to different KPIs. Visualizing the contribution of individual channels or initiatives helps marketers prioritize investments, allocate budgets effectively, and optimize resources.
This can also help multichannel marketing analysis, identifying the best variance in marketing activities and optimizing that mix for the greatest impact.
Budget optimization
Budget optimization helps marketers strategically allocate resources across marketing channels and activities for a better ROI. Once marketers identify the balance between short-term revenue goals and long-term brand-building initiatives, they can optimize their budget allocations to drive both immediate sales impact and long-term brand equity.
By monitoring performance metrics and adjusting budgets in real-time, marketers can ensure that resources are distributed effectively to support the achievement of marketing objectives across the entire marketing mix. Overall, budget optimization plays a crucial role in driving efficiency, effectiveness, and profitability in marketing campaigns and initiatives.
Pros and cons of marketing mix modeling
Marketing mix modeling offers several advantages for businesses that optimize their marketing strategies and allocate resources effectively. One of the primary benefits of MMM is its data-driven approach. MMM enables marketers to prioritize investments and allocate budgets strategically by understanding the impact of various marketing activities on KPIs like sales, ROI, and market share.
MMM also offers a holistic view of marketing performance by considering multiple variables simultaneously. By understanding the impact of different marketing, MMM helps marketers understand multichannel marketing effectiveness.
However, marketing mix modeling also has its limitations and challenges. One of the main drawbacks of MMM is its reliance on data availability and quality. Getting accurate and comprehensive data from various sources can be challenging, especially for small or emerging businesses with limited resources. If your data is inaccurate or incomplete, it can lead to an inaccurate MMM or bias in the results.
Next Steps
As helpful as the first round of understanding from the MMM can be, it’s important to continuously adjust your MMM process. It can change based on shifting objectives, feedback, new or improved data, and changing market conditions to drive continuous improvement in marketing effectiveness. While it may seem like a large undertaking at the outset, the insights gained by identifying a key objective and a better view of market drivers are well worth the effort.

All in all, marketing mix models can help further unlock the potential of your multichannel mix, fuel growth, and keep you ahead of the curve as the marketing landscape evolves without third-party cookies.
Learn how to strategize for a cookieless landscape in 2024, or let’s talk about achieving more for your marketing—and your business.